4. Test simulations¶
These are a number of computationally rather inexpensive test simulations, of which the run-specs header files are contained in the SICOPOLIS repository.
- Run
repo_vialov3d25 - 3D version of the 2D Vialov profile (Vialov [59]),SIA, resolution 25 km, \(t=0\ldots{}100\,\mathrm{ka}\).Similar to the EISMINT Phase 1 fixed-margin experiment (Huybrechts et al. [41]), but without thermodynamics. Instead, isothermal conditions with \(T=-10^{\circ}\mathrm{C}\) everywhere are assumed.
- Run
repo_emtp2sge25_expA - EISMINT Phase 2 Simplified Geometry Experiment A,SIA, resolution 25 km, \(t=0\ldots{}200\,\mathrm{ka}\) (Payne et al. [51]).The thermodynamics solver for this run is the one-layer melting-CTS enthalpy scheme (ENTM), while all other runs employ the polythermal two-layer scheme (POLY) (Greve and Blatter [31]).
- Run
repo_grl16_bm5_ss25ka - Greenland ice sheet, SIA, resolution 16 km,short steady-state run (\(t=0\ldots{}25\,\mathrm{ka}\)) for modern climate conditions (Fig. 4.1; unpublished).
- Runs
repo_grl16_bm5_{init100a, ss25ka_nudged} - Greenland ice sheet, SIA, resolution 16 km;\(t=-100\,\mathrm{a}\ldots{}0\) for the init run without basal sliding (…_init100a),\(t=0\,\ldots{}25\,\mathrm{ka}\) for the main run (…_ss25ka_nudged),steady-state run for modern climate conditions, free evolution during the first 10 ka, after that gradual nudging towards the slightly smoothed present-day topography computed by the init run (Fig. 4.1; unpublished).
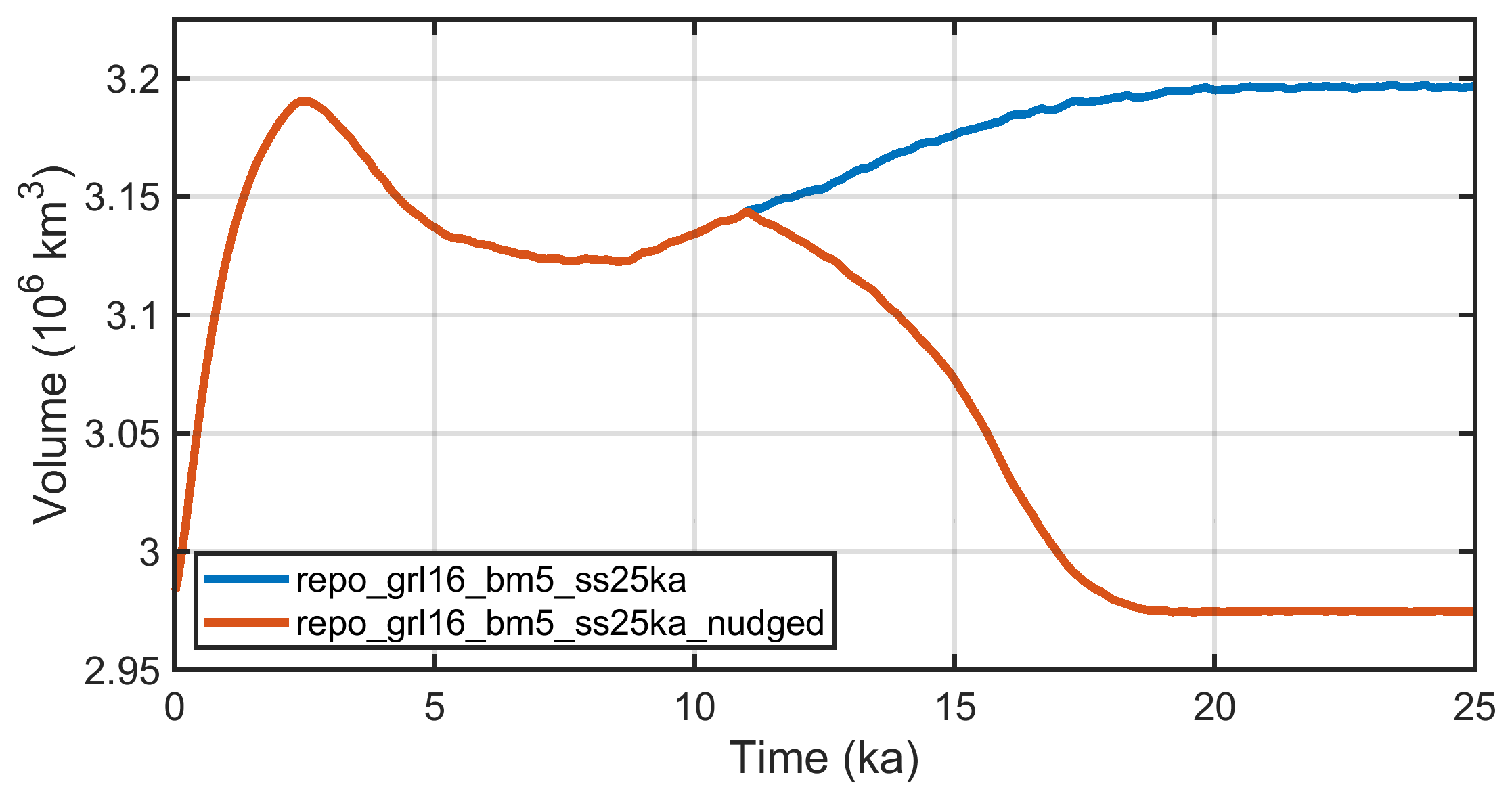
Fig. 4.1 Ice volume for the two steady-state simulations for Greenland, repo_grl16_bm5_ss25ka (unconstrained evolution) and repo_grl16_bm5_ss25ka_nudged (topography nudging with time-dependent relaxation time after t = 10 ka).¶
- Run
repo_ant64_bm3_ss25ka
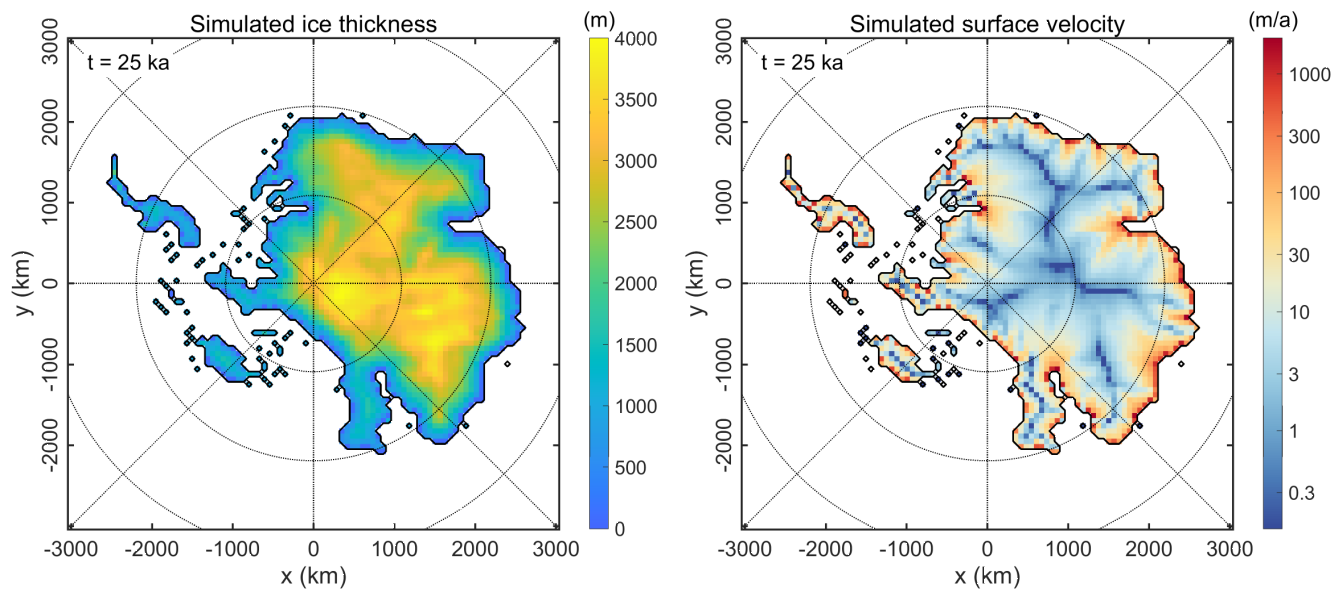
Fig. 4.2 Ice thickness and surface velocity for the short steady-state simulation for Antarctica with instantaneous removal of ice shelves (“float-kill”), repo_ant64_bm3_ss25ka. The West Antarctic ice sheet has largely disappeared.¶
- Run
repo_grl20_b2_paleo21 - Greenland ice sheet, SIA, resolution 20 km,\(t=-140\,\mathrm{ka}\ldots{}0\), basal sliding ramped up during the first 5 ka.Modified, low-resolution version of the spin-up for ISMIP6 InitMIP (Greve et al. [33]).
- Runs
repo_grl10_b2_{paleo21, future21_ctrl, future21_asmb}
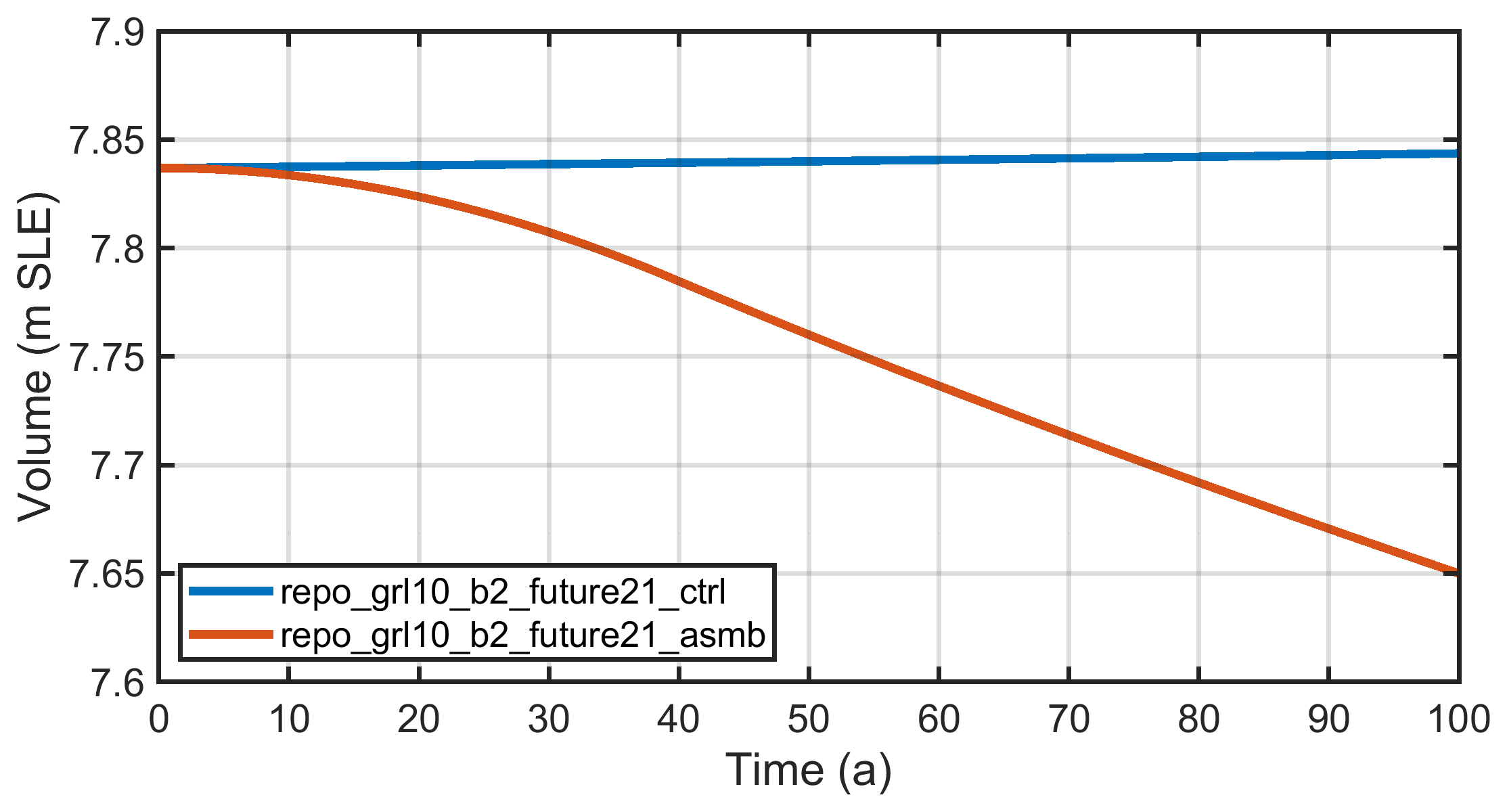
Fig. 4.3 Ice volume above flotation, expressed in metres of sea-level equivalent (m SLE), for the two ISMIP6 InitMIP future-climate simulations for Greenland, repo_grl10_b2_future21_ctrl (constant-climate control run) and repo_grl10_b2_future21_asmb (schematic surface-mass-balance anomaly applied).¶
- Runs
repo_ant64_b2_{spinup09_init100a, spinup09_fixtopo, spinup09, future09_ctrl, future09_asmb, future09_abmb} - Antarctic ice sheet with hybrid shallow-ice–shelfy-stream dynamics(Bernales et al. [5]) and ice shelves (SSA), resolution 64 km;\(t=-140.1\ldots{}-140\,\mathrm{ka}\) for the init run without basal sliding (…_init100a),\(t=-140\,\mathrm{ka}\ldots{}0\) for the run with almost fixed topography (…_fixtopo), basal sliding ramped up during the first 5 ka,\(t=-0.5\,\mathrm{ka}\ldots{}0\) for the final, freely-evolving-topography part of the spin-up (…_spinup09),\(t=0\ldots{}100\,\mathrm{a}\) for the three future runs (…_future09_{ctrl, asmb, abmb}).64-km version of the spin-up and schematic future climate runs for ISMIP6 InitMIP
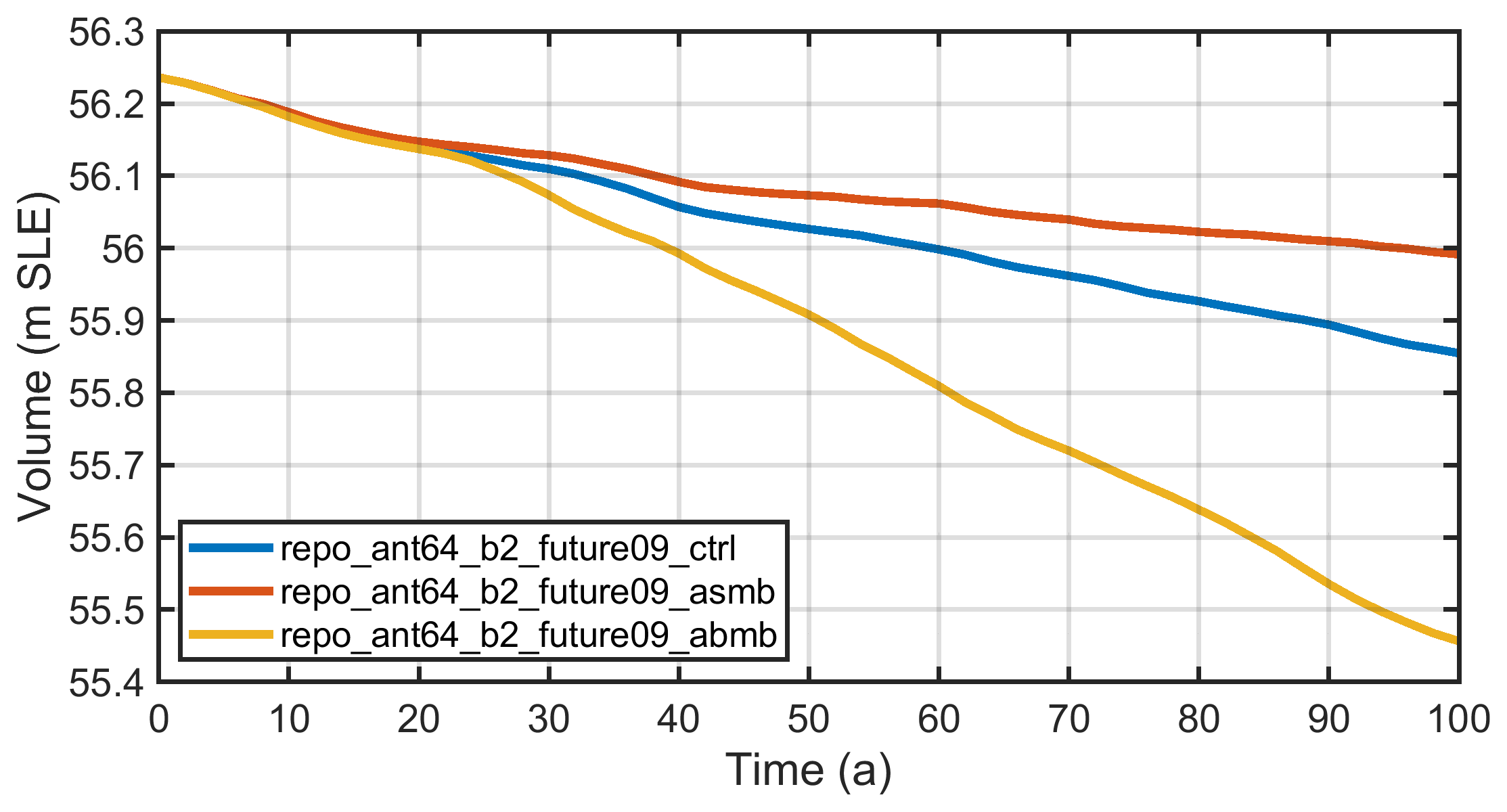
Fig. 4.4 Ice volume above flotation, expressed in metres of sea-level equivalent (m SLE), for the three ISMIP6 InitMIP future-climate simulations for Antarctica, repo_ant64_b2_future09_ctrl (constant-climate control run), repo_ant64_b2_future09_asmb (schematic surface-mass-balance anomaly applied) and repo_ant64_b2_future09_abmb (schematic sub-ice-shelf-melt anomaly applied).¶
- Runs
repo_asf2_steady,repo_asf2_surge - Austfonna, SIA, resolution 2 km, \(t=0\ldots{}10\,\mathrm{ka}\).Similar to Dunse et al. [15]’s Exp. 2 (steady fast flow) and Exp. 5 (surging-type flow), respectively.
- Runs
repo_nmars10_steady,repo_smars10_steady - North-/south-polar cap of Mars, SIA, resolution 10 km, \(t=-10\,\mathrm{Ma}\ldots{}0\).Steady-state runs by Greve [29].
- Run
repo_nhem80_nt012_new - Northern hemisphere, SIA, resolution 80 km, \(t=-250\,\mathrm{ka}\ldots{}0\).Similar to run nt012 by Greve et al. [40].
- Run
repo_heino50_st - ISMIP HEINO standard run ST, SIA, resolution 50 km, \(t=0\ldots{}200\,\mathrm{ka}\) (Calov et al. [12]).
Model times, time steps, computing times:
Run |
Model time |
Time step† |
CPU time |
|---|---|---|---|
repo_vialov3d25 |
\(100\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(20\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1.0\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_emtp2sge25_expA |
\(200\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(20\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(4.7\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_grl16_bm5_ss25ka |
\(25\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(10.9\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_grl16_bm5_init100a |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1.6\,\mathrm{sec}\) |
repo_grl16_bm5_ss25ka_nudged |
\(25\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(11.0\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_ant64_bm3_ss25ka |
\(25\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(2\,/\,10\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(8.9\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_grl20_b2_paleo21 |
\(140\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(0.9\,\mathrm{hrs}\) |
repo_grl10_b2_paleo21* |
\(9\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(1\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1.1\,\mathrm{hrs}\) |
repo_grl10_b2_future21_ctrl |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1.0\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_grl10_b2_future21_asmb |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1.0\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_spinup09_init100a |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(2\,/\,10\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(4.3\,\mathrm{sec}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_spinup09_fixtopo |
\(140\,\mathrm{ka}\) |
\(3.\bar{3}\,/\,10\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(0.9\,\mathrm{hrs}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_spinup09 |
\(500\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,/\,5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(0.7\,\mathrm{min}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_future09_ctrl |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,/\,5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(9.7\,\mathrm{sec}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_future09_asmb |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,/\,5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(9.7\,\mathrm{sec}\) |
repo_ant64_b2_future09_abmb |
\(100\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(1\,/\,5\,\mathrm{a}\) |
\(10.2\,\mathrm{sec}\) |
multi_sico_1.sh, run with SICOPOLIS v24 (revision bdf61628b) and the Intel Fortran compiler 2021.8.0 for Linux (optimization options -xHOST -O3 -no-prec-div) on a single core of a 12-Core Intel Xeon Gold 6256 (3.6 GHz) PC under openSUSE Leap 15.5.